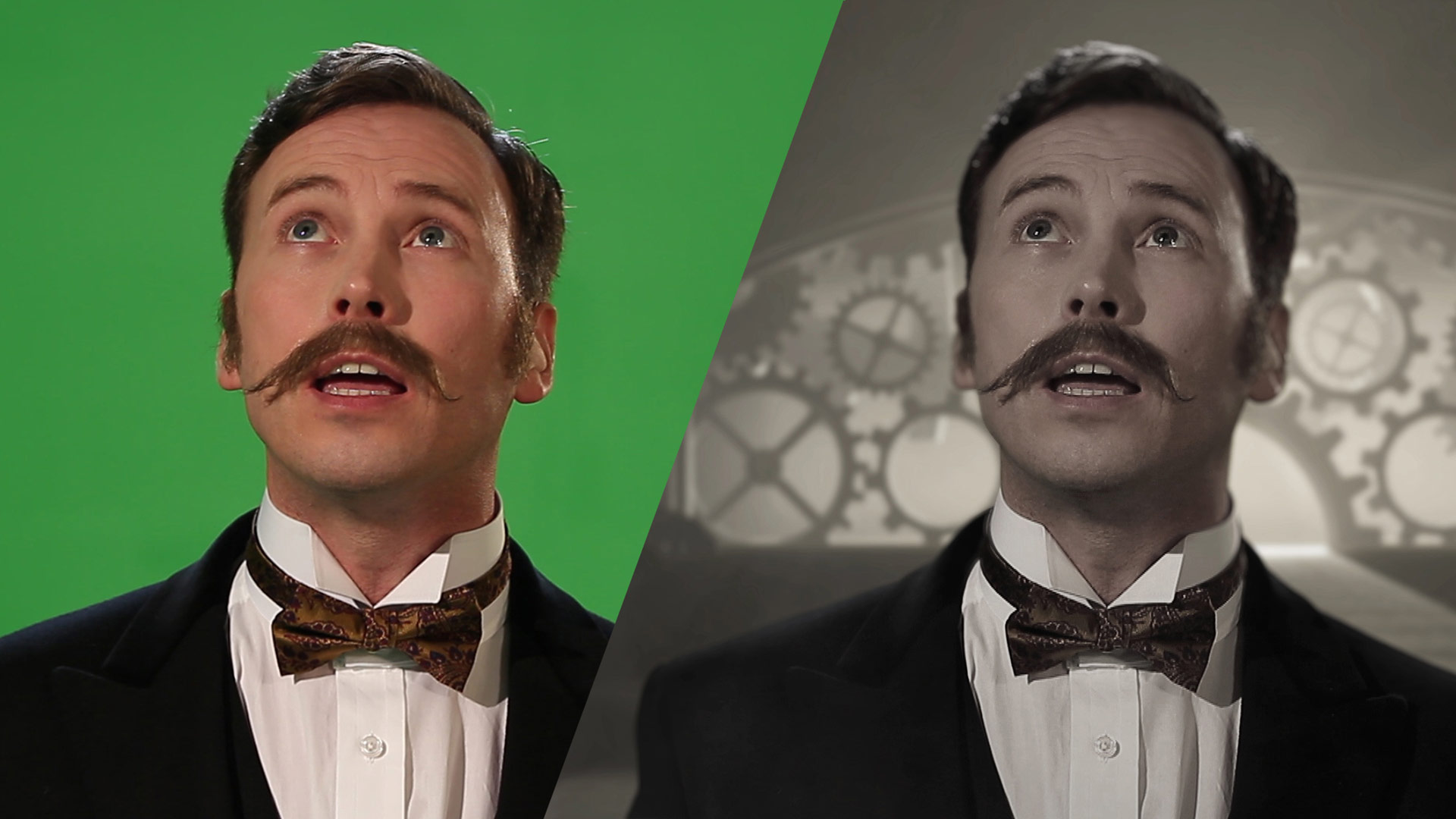
From Vision to Reality: Rob on the Roots of AR Media
‘Yes Sir, I can go to Texas and tour the states for 4 weeks filming’
We sat down with Director of AR Media, Rob Fairhurst, for a broader conversation on the history of our company. Find out more below.

Rob, can you tell us a little more about what inspired you to start a media production company?
Rob: I have loved filming things since I was a teenager - my friends and I would choreograph and film martial arts scenes and I still have the lumps to prove it! We would also go off and film comedy shows and concerts. I just loved getting to see the world through a lens and realised it afforded some very unique opportunities. I wanted to be a camera operator first and foremost; seeking projects that I felt passionate about. To do this, it meant creating a business around that.
Was there a specific moment when you knew this was the right path?
Rob: I assisted a group of filmmakers in making a horror feature film back in 2000. It was amazing because they were creatively up for anything... we had an absolute blast and I learnt so much in the space of that one film, making friends for life. We have a hundred stories to tell, plus, I even fell in love with one of them. You ask how I knew this was the right path, how could it be wrong?!
What gap in the industry were you hoping to fill when you launched the company?
Rob: To be honest I had no idea, I was caught somewhere in the middle between shooting music videos and wanting to really make longer length stories for audiences. We headed to Cannes and made short films of all sorts trying to figure it out.
What was the original vision for the company, and how has it evolved over time?
Rob: The original idea behind AR Media was to create visually interesting music-narrative videos, with the goal of eventually moving into some form of filmmaking. But, as we started producing more content for industrial companies we found ourselves filming in the most incredible locations - places you’d never normally get access to.
We shot everywhere from inside nuclear submarines and underground silver mines to solar plants in the Spanish desert and even on the deck of a newly built aircraft carrier. It was surreal. We were given opportunities to experience things most people never would.
I brought the energy and naivety of a young music video director into the world of corporate and industrial shoots - and honestly, I loved every minute of it.
As the company evolved, we embraced new technologies and produced high-quality content across AR, VR, mixed reality, and 360 video. But at heart, I’ve always been a filmmaker.
Now, we’re entering a completely new chapter - with AI changing everything. It feels like we’re on the edge of something truly transformative.
What were some of the biggest challenges you faced in the early days?
It was the boring stuff, really... contracts, budgeting, learning about tax returns, VAT, corporation tax, carnets… all those dull but absolutely necessary things that come with running a business.
Can you share a pivotal moment in the company’s journey that really shaped its direction?
Rob: Working with Jeff Wayne was a real highlight. My brothers and I used to listen to The War of the Worlds before bed when we were about 9 or 10. It absolutely terrified us, but we loved it!
Now, to have the chance to work on the animation for Jeff Wayne’s Musical Version of The War of the Worlds feels like a full-circle moment. It connects my childhood to my future.
Being trusted to design sequences for his arena tour - and later, to create scenes featuring Liam Neeson and other guest artists over the next 12 years was incredible.
But what stood out most was Jeff himself. He was a huge inspiration. His work ethic, his openness to collaboration, and the way he approached every project with the enthusiasm of a child – it's infectious! It was, and still is, a great experience. Nothing but respect.
How did you secure your first big client or project?
Rob: I said: 'Yes Sir I can go to Texas and tour the states for 4 weeks filming'... which led to 12 years of non-stop projects.
How would you describe the company culture and what do you think makes it unique?
Rob: We’re relaxed, non-competitive and non-micromanaging, I just don't think it helps.
If you could go back and give yourself one piece of advice at the start, what would it be?
Rob: I'm not sure how to answer this one, because I like the uncertainty of it all! I don't want to know the answers and find that it’s a bit more thrilling not knowing what's coming.
Maybe the fear is what drives us.
Where to host video
Video in marketing series Part 3 of 3
Catch up on the whole series: Video in Marketing
Part 1: How-does-video-marketing-compare-with-other-mediums
Part 2: What kind of video will work for you?
How does video marketing compare with other mediums?
Video in Marketing Series Part 1 of 3
We produce video. We concept, storyboard, produce, film, edit and deliver video. Happily for us, it’s a growing media. According to Cisco: 82% of Global Internet Traffic in 2022 Came From Video* But just saying it doesn't make it real, so we've put together a series of guides on how does video marketing compare, why, how and what video you should be considering.
Video marketing has shown significant effectiveness compared to other mediums in terms of engagement, reach, and conversion rates. Here's a general overview of the advantages of video marketing compared to other mediums:
Higher Engagement Rates: Videos tend to capture and maintain audience attention better than text or images. According to various studies, videos have higher engagement rates on social media platforms and websites.
- Videos typically receive higher engagement rates than text or image-based content on social media platforms.
- Viewers retain 95% of a message when they watch it in a video, compared to 10% when reading it in text.
- Social media posts with videos have 48% more views.
Improved Conversion Rates: Video content can lead to higher conversion rates. Research has shown that including a video on a landing page can increase conversion rates by a significant percentage.
- Adding a product video to a landing page can increase conversions by 80% or more.
- Video can lead to a 200-300% increase in click-through rates in email marketing campaigns.
- 64% of consumers are more likely to buy a product online after watching a video about it.
Better Information Retention: People tend to remember visual content more effectively than text-based content. This means that your messaging is more likely to stick with your audience when presented in video format.
- Video content generates 1,200% more shares than text and images combined.
- 80% of users can recall a video ad they viewed in the past 30 days.
- Social video generates 1,200% more shares than text and images combined.
Enhanced SEO: Video content can positively impact your website's search engine optimization (SEO). Google and other search engines often prioritize video content in search results.
- Video content is 50 times more likely to drive organic search results compared to plain text.
Increased Social Sharing: Videos are highly shareable on social media platforms. Engaging and informative videos can quickly go viral, leading to increased brand exposure.
- YouTube is the second-largest search engine after Google, making it a valuable platform for search visibility.
- Facebook users watch over 8 billion videos daily.
- LinkedIn users are 20 times more likely to share a video on the platform than other types of posts.
Personal Connection: Videos can create a stronger emotional connection with your audience. Seeing and hearing people, products, and services can lead to a deeper sense of connection and trust.
- Live streaming offers a sense of authenticity and immediacy, allowing businesses to showcase their expertise and connect with their audience on a personal level.
Mobile-Friendly: With the rise of mobile device usage, videos are easily consumable on smartphones and tablets. Mobile users are more likely to engage with video content while on the go.
- Mobile video consumption rises by 100% every year.
- 92% of mobile video consumers share videos with others.
Global Reach: Video content has the potential to reach a global audience, making it an effective tool for businesses looking to expand their market presence.
- 92% of B2B customers watch videos online, and 43% of B2B buyers watch video content while researching products and services for their business.
- 83% of marketers say video content is becoming more important.
Live Interaction: Live streaming and interactive videos allow for real-time engagement with your audience, fostering a sense of community and immediacy.
- 80% of audiences prefer watching live video content from a brand over reading a blog.
- 67% of viewers who watched a live stream purchased a ticket to a similar event the next time it occurred.
Analytics and Insights: Many video hosting platforms provide detailed analytics, allowing you to track viewer behaviour, engagement rates, and other valuable metrics.
So, looking at how does video marketing compare there's a lot going for it and it can have a positive impact on marketing, social, websites and your business in general. Decide which factors mean the most to you and set your online presence and processes up ready to make the most of your video. It's important to note that the effectiveness of video marketing can depend on factors such as your target audience, industry, and the quality of your content.
Catch up on the whole series: Video in Marketing
Part 2: What kind of video will work for you?
Part 3: Where to host your video
AR Media's A to Z of video production terminology
Goobledegook… It's all very well using industry terminology between ourselves but we realise that sometimes we may use terms that our clients may not understand. So here's our A to Z of things you might hear us say when you commission us for a video project.
 |
Aspect Ratio: The proportional relationship between the width and height of a video frame. Modern videos tend to use 16:9, pre-2000s you might have used 4:3. (also included in the A to Z as its what the AR of AR Media stands for |
 |
B-roll: Additional footage used to support the main content of a video. It is often used to provide visual context or cover transitions. We often capture manufacturing processes, buildings, people at work for this. Bokeh: A favourite of cinematographers, bokeh is the blur effect seen predominantly on lights that are out-of-focus. |
 |
Colour Grading: The process of adjusting and enhancing the colours of a video during post-production to achieve a desired look or mood. The footage we capture in its raw format has a very flat/grey look, but this allows us to tweak the colours to make them as realistic as possible. |
 |
Depth of Field: The range of distance in a shot that appears in focus. A shallow depth of field has a narrow focal range, while a deep depth of field has a wider focal range. Filming an interview for example you would use a shallow depth of field to keep the subject in focus but the background intentionally blurry. |
 |
Exposure: The amount of light that reaches the camera's image sensor, determining the brightness or darkness of a video. A correctly exposed shot will display depths of black without blowing out any highlights such as clouds in the sky. |
 |
Frame Rate: The number of individual frames captured or displayed per second. Common frame rates include 24, 30, and 60 frames per second (fps). This has an effect on quality and also file size. |
 |
Grip: A member of the production crew responsible for setting up and maintaining equipment such as lighting fixtures, tripods, and camera rigs. We're a tight-knit team so every one of us gets involved in setup and breakdown. Gimbal: A device that holds the camera and allows us to turn in any direction freely and smoothly. |
 |
High Definition (HD): A video format with a higher resolution than standard definition, typically 720p or 1080p. But of course these days we record even higher in 4K. |
 |
ISO: The sensitivity of a camera's image sensor to light. A higher ISO allows for better low-light performance but may introduce more noise into the image. A low ISO makes for a finer picture but needs little movement in the frame. |
 |
Jump Cut: A jarring transition between two shots that are nearly identical, often used for stylistic effect or to compress time. J-cut: When the image of a scene is preceded by its sound or audio content. |
 |
Key Light: The primary light source used to illuminate the subject in a video. We'll often have a 3 light setup to balance the subject. |
 |
Lens: A must-have of every A to Z, the optical device that focuses light onto the camera's image sensor. Different lenses have various focal lengths and characteristics, affecting the perspective and field of view. Lavalier: A microphone that clips to the presenter's clothing |
 |
Montage: A sequence of rapidly edited shots, often used to condense time, convey a series of events, or evoke emotions. |
 |
Non-linear Editing: The process of assembling and manipulating video clips out of chronological order using computer-based editing software. |
 |
Overexposure: When a video is too bright due to excessive light, causing details in the highlights to be lost. |
 |
Pan: The horizontal movement of the camera while it remains in a fixed position. We often use rails to slide the camera smoothly for this. Prime lens: a lens that uses a fixed focal length. These tend to be very high quality, very expensive and offer wide apertures. |
 |
QuickTime: A multimedia container file format developed by Apple, commonly used for video editing and playback. |
 |
Rack Focus: The technique of changing the focus from one subject to another within the same shot to shift the viewer's attention. |
 |
Storyboard: A visual representation of a video's planned shots or scenes, typically consisting of illustrations or images with accompanying descriptions. We can help you create these. Shotgun mic: Often used for broadcasting, TV and film production, sports and other applications where it is impractical or undesirable for the subject to wear or hold a microphone. |
 |
Tracking Shot: A shot in which the camera moves alongside or follows a subject, often achieved using a dolly or a stabilized gimbal. |
 |
Underexposure: When a video is too dark due to insufficient light, causing details in the shadows to be lost. |
 |
Voiceover: A recorded narration or commentary added to a video during post-production, typically synchronized with on-screen visuals. We have a full recording studio in our building for this. |
 |
White Balance: The adjustment of a camera's settings to ensure accurate color reproduction under different lighting conditions. |
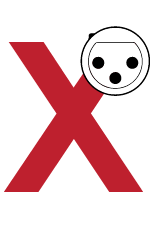 |
XLR: A type of professional audio connector commonly used for balanced audio signals in video production. |
 |
YouTube: We couldn't have an A to Z without mentioning a certain popular online video-sharing platform where users can upload, view, and share videos. Alternatives include Vimeo and Wistia. |
 |
Zoom: The change in focal length of a camera lens to make the subject appear closer or further away without physically moving the camera. Zoom shot: The illusion of moving closer or away from a subject, making them appear bigger or smaller. |
So there you have a brief A to Z of video terminology, enjoy and we hope you find it useful.
Corrections - what we can and can't do in post
When editing a video, there are certain corrections that can be made, as well as limitations on what can be achieved.
Here are some common corrections that can be made during video editing:
- Trimming and cutting: We can remove unwanted sections from the video, such as mistakes, pauses, or unnecessary footage. We can also cut between cameras or screen footage to improve interest and switch between takes if there's a stumble in delivery.
- Colour correction: Adjusting the colour and contrast of the video can enhance its overall look and feel. We can fix issues like white balance, exposure, saturation, and tint. We intentionally film in a flat colour format which means the 'rushes' might appear a little washed out. But, this gives us the biggest dynamic range to adjust colours in post.
- Audio adjustments: We can modify the audio levels, reduce background noise, and apply filters or effects to enhance the sound quality. But, the better the audio at the point of record, thee better the final output will be, too many cuts between takes starts to look jarring to the viewer.
- Stabilization: If the footage is shaky or unstable, we can use video stabilization techniques to smooth out the motion. We often use equipment with a built-in gimbal for stabilisation.
- Transitions and effects: Video editing software provides a variety of transitions and effects to enhance the visual appeal and flow of the video.
- Text and titles: We can add text overlays, titles, subtitles, or captions to provide information or improve the viewer's understanding. We often call these 'Lower-thirds'
- Speed adjustments: Video editing allows us to change the playback speed of clips, creating slow-motion or time-lapse effects. For super slo-mo effects these require specialist cameras operating at incredibly high frame rates.
- Cropping and resizing: We can crop or resize the video frame to focus on specific areas or adjust the aspect ratio for different platforms. By filming in 4k resolution we can crop into areas and the end result will likely remain as HD, but to avoid pixelation, the higher resolution the better at the start.
However, there are certain limitations to what can be achieved during video editing:
- Resolution limitations: The quality of the original footage sets the upper limit for the final video quality. Editing cannot magically improve the resolution beyond what is captured initially. There are methods to up-res footage but these should be used as a last resort as the quality will decrease.
- Overexposed or underexposed footage: While some adjustments can be made to correct exposure issues, severely overexposed or underexposed footage may be challenging to salvage.
- Focus issues: If the footage is out of focus, it is difficult to recover sharpness during editing. We can make slight improvements, but it may not fully restore the intended focus.
- Missing or distorted footage: If the video is missing essential parts or suffers from severe distortion, editing can only do limited corrective measures. In such cases, re-shooting or using alternative footage may be necessary.
- Audio quality: Editing can improve audio to some extent, but if the original recording has significant background noise or distortion, complete restoration may be difficult.
Overall, video editing offers a wide range of corrections, but it's important to have high-quality source material to achieve the best results. Aim to get the best footage at the start to avoid noticeable jumps in sequence, colour mismatches between scenes and to avoid extending costly editing time.
How much does video cost?
You know what we're going to say, don't you? How long is a piece of… videotape.
Well, videotape is long gone and so have some of the prohibitive cost of making videos. Kit is smaller, lighter and you can move quickly but as you can imagine, costs can still vary wildly depending on the project specifics and it's all about the detail.
The below costs are ballpark figures, actual projects can vary wildly in complexity and procedures.
Video testimonial costs
 Ideally, you'd be looking at a 2 person team (director and a skilled lighting camera operator) and at least 2 cameras. Setup time will be around 2 hours, filming will probably take around 1 - 2 hours and acquiring some strong B-roll footage would likely take another couple of hours. You could expect to get a first draft around 3 working days later and with up to 2 rounds of amends your finished article could be available 7 working days later.
Ideally, you'd be looking at a 2 person team (director and a skilled lighting camera operator) and at least 2 cameras. Setup time will be around 2 hours, filming will probably take around 1 - 2 hours and acquiring some strong B-roll footage would likely take another couple of hours. You could expect to get a first draft around 3 working days later and with up to 2 rounds of amends your finished article could be available 7 working days later.
Cost: in the region of £4,000
The cost of Animation
With a bespoke animation, a lot of the cost is in the pre-production and design stages. You're aiming really to get the script and storyboard as close to the final thing before production starts so the animators are only making assets and movements once. With a good brief and responsive sign-off procedure, a script and storyboard could take a minimum of 3 working days. Depending on the complexity and if assets need creating or not, the first draft animation could take a further 5 days. Amends and voiceovers might take another 2 days and a final animation could be ready within 10 working days from start to finish.
Cost: in the region of £6,000
Corporate video cost
This can be a very open brief, but if we take the 2 routes a corporate video often takes we can put some guesswork in. The cheaper route might involve writing the script, storyboarding and arranging voiceovers, product demos and stock footage. From a good brief, this could take 10 working days and have a cost of around £5,000 (not including stock footage costs). The more creatively crafted and professional route might mean filming which means crew, travel. If we consider additional motion graphics, maybe some drone capture and a lot of creative editing.
This could easily take 20 working days and have a cost of around £15,000
Product launch or commercial

If you want to get really creative this is where it's at. It could involve a lot more project management, shooting footage in multiple locations, building sets, arranging actors and props, recording voice overs, applying visual effects all with some incredible attention to detail. The result will be unique, highly polished and have creative flair, but this takes time.
You could expect to take 30 working days and require a budget of around £35,000.
These are all finger-in-the-air costs and timescales, but we hope they at least give you some sort of idea of how affordable or expensive video can be in general.
Want to get in touch?





